positive drop arm test|drop arm test sensitivity specificity : solutions Learn how to perform the Drop Arm Test, a test for rotator cuff tears, specifically of the supraspinatus tendon. See the involved structures, test movement, positive test criteria, . WEBO Imbatível 2 - O Lutador - Dublado - BluRay-Rip - 1,35 GB - 720p - 2006 MEGA----> Parte 01 - Parte 02 - Parte 03. Postado por Thiago Silva às 16:43. Nenhum comentário: Postar .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBPhotos. See all photos. Caesars Slots. 5.6M likes. 100% FREE video slots and casino .
The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus . This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when . See moreThe test is negative if the patient is able to control the lowering of the arm slowly and without their symptoms occurring . It is a positive test if there is a sudden dropping of the arm or weakness in maintaining arm position during the eccentric part of abduction. There . See moreIt was found that it is unclear if a full thickness rotator cuff tear can be diagnosed by using any of the cluster of lag signs, let alone solely the drop arm sign . All lag sign tests for rotator cuff integrity have been shown to have high specificity, but low . See moreSensitivity of detecting a full thickness supraspinatus tear is 73% The specificityis 77% The Likelihood Ratio is 6.45 (95% CI=2.25–18.47) See more
Learn how to perform the Drop Arm Test, a test for rotator cuff tears, specifically of the supraspinatus tendon. See the involved structures, test movement, positive test criteria, . This article reviews the anatomy, history and physical examination of the shoulder, including provocative testing for impingement syndrome and glenohumeral instability. The positive drop arm test is one of the maneuvers . Positive result: Weakness or pain in your shoulder. Neer’s sign. How it’s performed: A doctor will stabilize your scapula, rotate your arm internally, and flex your arm. What it tests.Learn how to perform and interpret the drop arm sign, a test for full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons. See the sensitivity, specificity and clinical value of this test according to research studies.
The drop arm test is a simple test to diagnose rotator cuff injuries or weakness in the shoulder. It involves raising and lowering the arm at 90 degrees and . If your arm drops or moves, you have a positive lag sign and your supraspinatus, infraspinatus, or teres minor tendon may be compromised or torn. 4. Infraspinatus Test. Your . A positive drop arm test increases the likelihood of rotator cuff disease, but other tests are more accurate and specific. Learn about the evidence-based physical examination tests for diagnosing rotator cuff disease .If the patient's arm drops suddenly or experiences pain, then the test is considered positive. Codman's Test video provided by Clinically Relevant.
Learn how to perform and interpret the Drop Arm test for rotator cuff pathology. The test is positive if the patient cannot control the arm as it drops to their side or shows weakness at 90 degrees. A positive drop arm test is usually indicative of a tear in the rotator cuff muscles, particularly the supraspinatus muscle. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that help to stabilize the shoulder joint and facilitate movement. The supraspinatus muscle is one of these four muscles and is the most commonly affected muscle in rotator cuff .How to Interpret Drop Arm Test. Positive Finding: The test is considered positive if the patient is unable to control the arm as it drops to their side, or if significant weakness is noted when the examiner places pressure on the .
This is a really great test for you to use with your patients who you suspect may have injured their Rotator Cuff, and in particular, may have suffered a Rot.
positive hornblower's sign
The drop arm test works by going through subluxation via the humeral head looking for a tear or weakness in the supraspinatus tendon. [2] Results. A positive test is found if the patient cannot perform this motion of adducting the arm back to the body controllably or if the patient experiences pain while performing this test. [1] [2] ReferencesFor a positive test, however, the patient would not be able to hold this position and their arm may spring back anteriorly, indicating that the teres minor and the infraspinatus are weak or painful. 2. The examiner supports the elbow and holds the arm in external rotation at the wrist. 3. The patient is asked to hold the position while the . Drop Arm Test. A rotator cuff tear will make it difficult for you to control your arm as it lowers, especially if any one of the 4 stabilizers of the rotator cuff are compromised. . If your arm drops or moves, you have a positive lag sign and your supraspinatus, infraspinatus, or teres minor tendon may be compromised or torn. 4. Infraspinatus .
The cluster for a full thickness rotator cuff tear includes 1. the Drop-arm sign, 2. the painful arc sign, and 3. infraspinatus manual muscle test. If all three tests are positive, the +LR is 15.6. (Note is 3/3 are positive and the patient is greater than 60 years old the +LR increases to 28) If all three tests are negative the -LR is .16If the patient can lower the arm without problem, the test should be performed again and the examiner should apply a slight tap on the forearm when the arm is abducted at 90 0. Positive Test: This test will be positive if the patient can not control the adduction movement of the arm and the arm drops to the patient’s side. Speed’s test: A positive test consists of pain elicited in the bicipital groove when the patient attempts to forward elevate the shoulder against examiner resistance; the elbow is slightly flexed, and the forearm is supinated. . Drop arm test: The patient’s shoulder is brought into a position of 90 degrees of shoulder abduction in the .The first is a drop test: the clinician drops the “paralyzed” arm over the patient's face. In pseudoneurologic syndrome, the “paralyzed” arm will not strike the patient's face when dropped .
A positive drop arm test may also have neurologic causes, such as damage to the subscapular nerve, so the patient must be thoroughly examined from a neurologic standpoint. In lesions of the supraspinatus muscle as a result of chronic degenerative processes, the drop arm test may be falsely negative due to muscular compensation, especially by . Drop Arm Test . Your healthcare provider may perform the drop arm test if they think you may have a rotator cuff tear in your shoulder. For this test, the provider will lift your arm out to the side of your body while keeping it straight. . They then drop your arm (hence the name of the test). The test is positive if you can't hold your arm .Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Empty Can Test, also known as the Jobe or Supraspinatus test, is used to assess for lesions of the rotator cuff, specifically the supraspinatus muscle and supraspinatus tendon.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patients arm is actively abducted to 90 o; The examiner applies downward resistance to the abducted arm; With the patient's hand in .Data in this study shows that if the drop arm test is positive one can almost be certain that the patient has a supraspinatus tear but a negative test does not provide conclusive information to the examiner. The drop arm test also cannot be used as a screening test due to its low sensitivity. This paradigm also applies to the lag signs for .
Drop-arm test: Active shoulder abduction to 90°, then return . Positive: Dropping the arm down with pain indicates a positive test; Drop Arm Test video provided by Clinically Relevant. Jobe/supraspinatus/empty can test: Resist shoulder abduction and internal rotation This Technique Peek video features Frank Hoeffner, DPT, OCS demonstrating how to perform drop arm test for the shoulder. This test is performed by passively . The drop arm test, also known as Codman's sign, was performed with the patient standing . The patient was asked to abduct the arm fully and then to reverse the motion slowly, in the same arc. When the arm dropped suddenly, the test was considered positive. The drop arm test was developed specifically for the evaluation of the supraspinatus tendon.
full thickness drop arm sign
This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests . In the cross-arm test, you raise your arm to shoulder level with your elbow flexed at a 90-degree angle. Then, keeping your arm in the same plane, you move it across your body at chest level. Kathleen Carr, MD demonstrates the Drop Arm Test as part of a complete Shoulder ExamThe Drop-Arm Sign. Patient actively elevates the arm in the scapular plane and then slowly reverses the motion. A positive test is defined as the patient experiencing pain during the activity or that the arm suddenly drops. The Painful Arc Sign (Fig 1) Patient fully elevates the arm along the scapular plane and then slowly reverses the motion.
A positive test result is considered to be the inability to maintain the arms at 90 degrees due to pain or weakness. When combined with other tests such as the Hornblower's sign, the external rotation lag sign, the internal rotation lag sign, and the empty/full can test, the drop arm test can yield greater accuracy.
Negative Test: The patient can smoothly and slowly lower the arm without difficulty, indicating the absence of significant rotator cuff pathology.; How the Drop Arm Test Helps in Diagnosing Rotator Cuff Tears? The drop arm test serves as a valuable screening tool for detecting rotator cuff tears, particularly involving the supraspinatus tendon.A positive test .
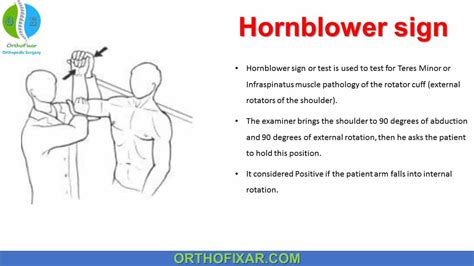
This test is also known as the Patte's Test. . or pain can indicate a tear. Technique [edit | edit source] The patient is in a standing position. The patient's arm is passively elevated to 90 degrees in the scapular plane, by the examiner . The test is positive if the patient is unable to perform external rotation, and thus indicates a tear .
The drop arm test has been reported to be 35% sensitive and 88% specific for full-thickness tears and 14.3% sensitive and 78% specific for partial-thickness tears. 39. . While maintaining this arm position, the patient is asked to externally rotate against resistance. A positive test occurs when the patient’s arm falls into IR.Drop arm test: it is used to test rotator cuff tears, specifically the supraspinatus. Empty can (Jobe) test: it is also used to assess the strength and function of the supraspinatus muscle . Hawkins-Kennedy test: it is used to test for shoulder impingement syndrome, when there is subacromial impingement of the supraspinatus tendon . Drop Arm Test is an orthopedic maneuver used to help diagnose injury to the rotator cuff. A positive test will involve the inability to gradually lower the .
dropping sign shoulder
drop arm test shoulder positive
WEBThe actual menu of the Sushi Ragueb restaurant. Prices and visitors' opinions on dishes.
positive drop arm test|drop arm test sensitivity specificity